| The hydronium ion is also referred to as the hydrogen ion. They are represented
as H+, since a hydrogen ion in an aqueous environment becomes
a hydronium ion.
H+(aq) + H2O (l)  H30+(aq)
H30+(aq)
Bases
are substances that
contain an OH group and that dissociates in water to release
hydroxide ions
(OH-). When strong acids and bases
come together they react so as to neutralize their acid and base properties
producing water and a salt. Some energy as heat can also be produced.
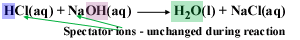
A
net ionic equation
is an equation that shows only the reactants ions that undergo a change during
the reaction.
For all acid and base neutralizations the net ionic equation is essentially
the same.
H+(aq) + OH-(aq)  H2O(l)
H2O(l)
Since the ions, like the sodium and chloride ions, (highlighted in the
full neutralization equation above), remain in solution as ions, they have not changed. Ions
that remain unchanged during a chemical reaction are referred to as spectator ions
Weak acids and bases do not dissociate completely in water and so release
fewer H3O+ or OH-.
The strength of acids and bases is measured on a pH
where:
pH = -log[H+ ],
The squared brackets indicate the concentration of whatever substances
is named between them. As a result of this equation, the higher
the hydrogen ion concentration is, the lower the pH will be. Substances
with very low pH's are acids. If the H+ concentration
is very low, the pH will be high. Substances with high pH values are bases.
The acid-base nature of water is an important component of acid-base
chemistry. Water actually behaves both as an acid and as a base.
Water obviously contains both H+ ions and OH- ions.
At equilibrium, the concentration of H+ in water is 10-7
moles/liter,
so we can calculate the pH of pure water as:
pH = -log[H+] = -log(10-7) = 7
Solutions with a pH of 7 are said to be neutral. Substances with pH
values below 7 are acidic, while those above a pH of 7 are basic.
In the atmospheric sciences, the acidity of rain water is of great interest.
Natural unpolluted rainwater is slightly acidic. It actually has
a pH of about 5.7. This is due to the absorption of carbon dioxide,
readily available in the atmosphere, to form carbonic acid, H2CO3.
|