pop up description layer



Next: Electro-Magnetic Shaker
Up: m1index
Previous: Amplitude and Phase of
 The small-scale model of the three-degree of freedom structure is shown to the right. Its properties are as follows:
The small-scale model of the three-degree of freedom structure is shown to the right. Its properties are as follows:
- It is made entirely of aluminum.
- Each of the four columns has cross section dimensions of
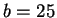 mm
mm 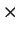
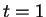 mm.
mm.
- Each story has a floor-to-ceiling clear height,
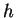 , of about 140 mm and the structural columns are tightly clamped
at each floor.
, of about 140 mm and the structural columns are tightly clamped
at each floor.
- The floors are rigid plates of aluminum, of about 1.1 kg each.
- The building model is placed on a table which can slide in one horizontal direction with almost no friction.
- This table is made to oscillate sinusoidally or randomly by an electro-magnetic shaker, described in the next section.
Theoretically, the shear stiffness of one column is 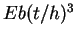 .
The resulting motion of the table (the 'ground') and each of the three degrees of freedom ('floors')
is measured with acceleration-sensing devices (called accelerometers), also described later.
When you click the "Run Experiment" button on the web browser, the shaker-amplifier warms up for about 5 seconds
and the WEAVE system commands the shaker to move in either a sinusoidal or random manner, as you choose from your web-browser.
As the shaker applies motion to the base of the structure, measurements of the ground accelerations and floor accelerations are captured at 100 times per second.
The experiment takes about 18 seconds to run, and as soon as the experiment is finished,
the measured accelerations are plotted to your web browser.
By clicking the "Download Experiment Data File Here" link, you may save the actual acceleration measurements (scaled to units of "g") to your computer for plotting and analysis.
.
The resulting motion of the table (the 'ground') and each of the three degrees of freedom ('floors')
is measured with acceleration-sensing devices (called accelerometers), also described later.
When you click the "Run Experiment" button on the web browser, the shaker-amplifier warms up for about 5 seconds
and the WEAVE system commands the shaker to move in either a sinusoidal or random manner, as you choose from your web-browser.
As the shaker applies motion to the base of the structure, measurements of the ground accelerations and floor accelerations are captured at 100 times per second.
The experiment takes about 18 seconds to run, and as soon as the experiment is finished,
the measured accelerations are plotted to your web browser.
By clicking the "Download Experiment Data File Here" link, you may save the actual acceleration measurements (scaled to units of "g") to your computer for plotting and analysis.
Subsections



Next: Electro-Magnetic Shaker
Up: m1index
Previous: Amplitude and Phase of
Henri P Gavin
2002-03-30
 The small-scale model of the three-degree of freedom structure is shown to the right. Its properties are as follows:
The small-scale model of the three-degree of freedom structure is shown to the right. Its properties are as follows:
 The small-scale model of the three-degree of freedom structure is shown to the right. Its properties are as follows:
The small-scale model of the three-degree of freedom structure is shown to the right. Its properties are as follows: