Investigation 1B:
Evaporation and Climate
Evapotranspiration
Overall Evapotranspiration Rates
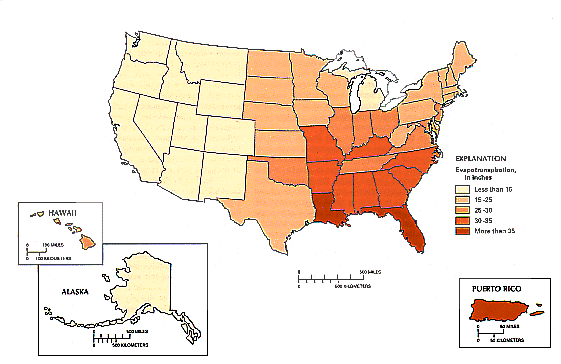
Most estimates of evapotranspiration are derived from studies of small areas (a few acres or less) where climate, available moisture, and plant cover are relatively uniform; thus, regional estimates are uncommon. However, the magnitude and distribution of mean annual evapotranspiration for regions of the United States have been estimated from hydrologic budgets given for each State in the 1987 National Water Summary (U.S. Geological Survey, 1990), as shown in Figure 5, below. The estimated mean annual evapotranspiration for each State was determined from the mean annual statewide values of four principal components of the hydrologic budget-precipitation, surface-water inflow, surface-water outflow, and consumptive use. All four components were measured or estimated, and evapotranspiration was computed as a residual of these components.
For the United States and Puerto Rico. the "estimated mean annual evapotranspiration" ranges from a maximum of 45 inches per year in Puerto Rico to a minimum of 7.6 inches per year in Alaska.
- Within the contiguous United States, what area has the greatest evapotranspiration rate?
- There is more solar radiation and lake evaporation in the Southwest than in most of the rest of the country, and yet it doesn't have the greatest evapotranspiration rate. Why not?
To continue to the Exploration Section of Investigation 1B: Evaporation and Climate, click on the link to the left.