An important part of engineering is knowing and understanding the materials that you work with. If an engineer uses the wrong material, there could be serious consequences. The Eiffel Tower, for instance, would collapse if it were made of a weaker material, such as lead. Engineers don’t build car engines out of wax because the heat would cause them to melt.
These examples may be obvious, but in many cases, the consequences of using the wrong material are not as clearly defined. Sometimes it may be a case of simply requiring more time and effort to work with or simply costing more, yet other times the wrong material can cause complete failure of a project.
One important aspect of a material is its density. Most of us have a basic understanding of density but may not know how to apply it to a scientific or engineering problem. This lesson will help students understand how an engineer would use density when designing a boat.
Review of surface area and volume of solid objects:
The surface area of an ordinary object, such as a box or cube, is the sum of the areas of the sides exposed to the elements. A closed box will have six surface areas exposed; an open box will have five. Care must be exercised when computing the surface
area of such objects to check whether the object has an open side. However, the volume of an open or closed box of the same dimensions will be the same. 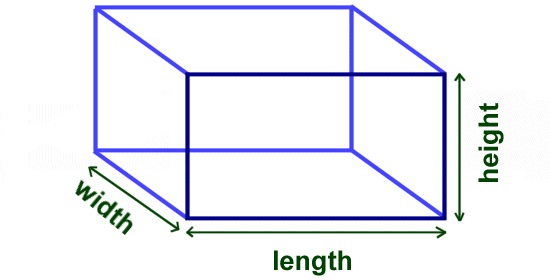
For example, an open box with dimensions L x W x H will have the same volume as a closed box with the same dimensions. For example, two boxes of dimensions 4” x 3” x 2” (L x W x H), one open and one closed, will have the same volume but different surface areas. The volume for each box will be 24 cubic inches, whereas the surface area for the open box may be 40 square inches if one of the 4” x 3” sides is missing and 52 square inches if the box is closed.
Next, we will explore why knowing the volume of an object is important.
| On to page 2! |