| |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide is another pollutant with both natural and
anthropogenic
origins. Sulfur dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere when
coal, oil,
and other sulfur containing fuels are burned. Major sources of
sulfur
dioxide are petroleum refineries, power plants, paper mills and
smelters.
Volcanic activity also releases around 109 kg of
sulfur per
year in the form of SO2. Sulfur dioxide can oxidize
to form
sulfur trioxide (SO3) and can react with moisture in
the air to
form sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Sulfuric acid
in the
atmosphere can also cause respiratory problems such as bronchitis
and
emphysema. Sulfuric acid is also deposited in the form of acid
rain which
can damage plant life, destroy man-made monuments and structures,
and
devalue personal property.
| Pollutant |
Source |
Effects |
| Natural |
Human |
| Sulfur
dioxide
(SO2) |
volcanic
eruptions |
petroleum
refineries, power
plants, paper mills, and smelters |
acid rain:
respiratory illnesses, damage to vegetation, destroy structures
|
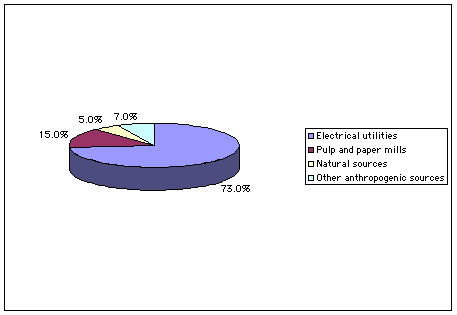
| The graphic at the right shows sources of SO2 for the United States. The majority of SO2 emissions come from electrical utilities, especially in the eastern part of the United States. Pulp and paper mills also contribute a fairly significant amount to the total SO2 emissions per year. Indeed, driving past a paper mill will quickly convince you that sulfur products are being emitted, assuming your sense of smell is functional! |
 |
 Graphic from US EPA
Graphic from US EPA |
The graphic at the left (click on graphic to see full-sized) shows SO2 emissions in the United States by county. This data comes from the US EPA National Air Quality Standards report. It is relatively clear that there is an abundance of high emissions counties in the eastern United States, especially throughout the Ohio Valley and up into the northeastern United States. |
Confused? Have a question? If so, check out the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) page or send mail to the OS411 tutor (os411tutor@shodor.org) with your question!
Report technical/content problems here
|
|