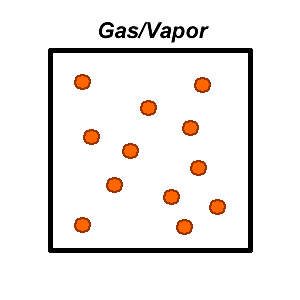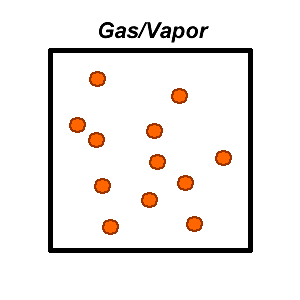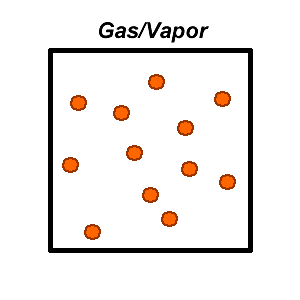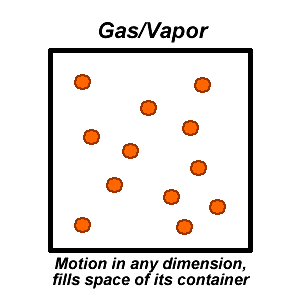
The Gas PhaseIn the gas phase, molecules of substance have very little effect on each other. The travel rapidly with little interferance until they encounter another gas molecule, an aerosol or a surface.Molecules move freely in all directions a very high speeds. Since molecules move freely, A gas will expand to fill an empty space moving from regions of high gas concentration to regions of low gas concentrations very quickly. This means that over a relatively short period of time, the concentration of gas molecules in a defined space will be uniform provided external conditions such as heat energy and pressure remain the same.
 Confused? Have a question? If so, check out the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) page or send mail to the OS411 tutor (os411tutor@shodor.org) with your question! Report technical/content problems here |
|
|