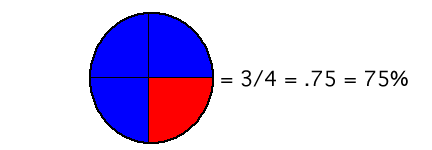Ideas for Working with Fractions
AbstractIt is necessary for fourth and fifth grade students to be able to convert between fractions, decimals, and percents. Much of this learning must be done through repetition and practice once students begin to grasp the concept. This lesson provides a way for students to practice this concept. ObjectivesUpon completion of this lesson, students will:
Standards Addressed:Student Prerequisites
Teacher Preparation
Key Terms
Lesson Outline
|