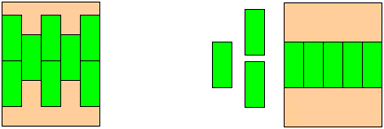
|
|
|
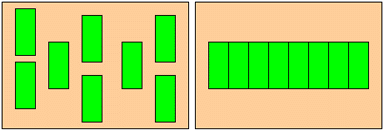
Alignment is a process that organizes all of the teeth into a smooth curve when looking down on the biting surfaces of the teeth. If you had a number of boxes and wanted to align them on a table, you could place them side-by-side.
Suppose the boxes were to be lined up on a table that was not big enough to hold all of the boxes in one line. To circumvent this problem, you could stack the boxes on top of each other to make them fit.
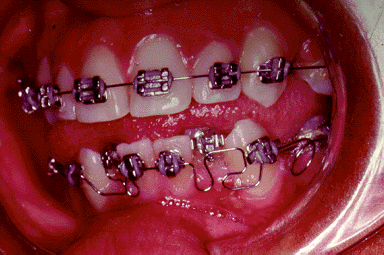
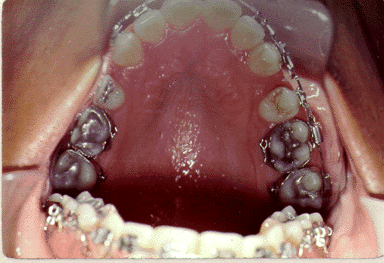
When a person does not have enough room in the mouth for all of the teeth, teeth will stack themselves so that they all fit into the mouth. This situation is known as crowding. Crowding occurs in the mouth when the jaws do not have enough space to hold all of the teeth in a smooth curve. Crowding results in teeth that are stacked on top of each other so that all of the teeth fit in the mouth.
The goal of alignment in orthodontic treatment is to correct crowding by lining up all of the teeth into a smooth curve. One major problem is to overcome the fact that there is not enough room in the mouth for all of the teeth. If all of the boxes do not fit on the table in a straight line, what could you do? Remove enough boxes so that the remaining boxes can all align on the table side-by-side.
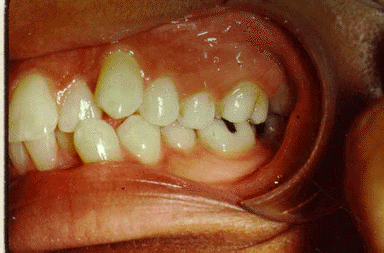
Notice the crowding of your patient. In order to align all of her teeth in a smooth curve, you must remove some teeth.
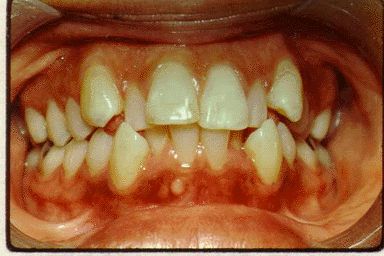
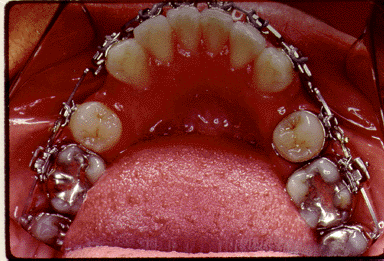
By removing teeth, you now have enough space to align all of her teeth in a smooth curve.
The process of alignment is accomplished by uncontrolled tipping of teeth into a smooth arch. Alignment requires a wire with the following specification:
high strength Shape:
Note:
Would you prefer a round or a rectangular wire? Size:
Note: 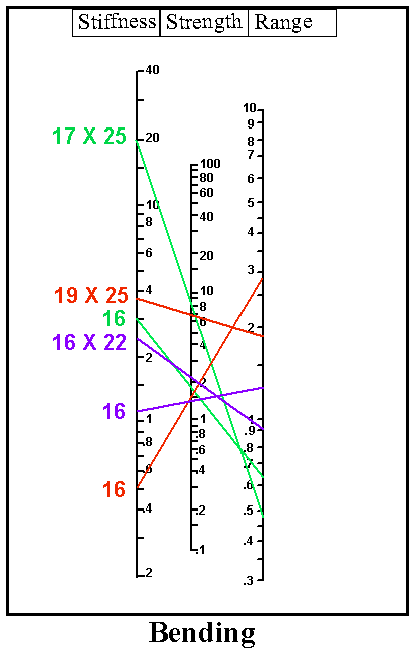
Which wire would work best for this phase? With the proper orthodontic technique, your patient's teeth will move to result in the following configuration:
Last Update: August 18,1998 Please direct questions and comments about this page to appl@net.chem.unc.edu Designed in cooperation with The Shodor Education Foundation, Inc. © Copyright 1998 The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill |